Good planning, diligent execution, timely and appropriate communication, and management of stakeholder expectations are all essential elements in delivering a project to completion. This simple statement belies the complexities involved in any project implementation.
In a 2014 NUS-ISS survey of IT project management practitioners in Singapore, the respondents indicated that 67% of their projects were considered successful, 27% were challenged and 6% were failed projects. This is upbeat compared to other international research studies where successful and challenged projects were about equivalent (about 40% each) with 18% of failed projects #1.
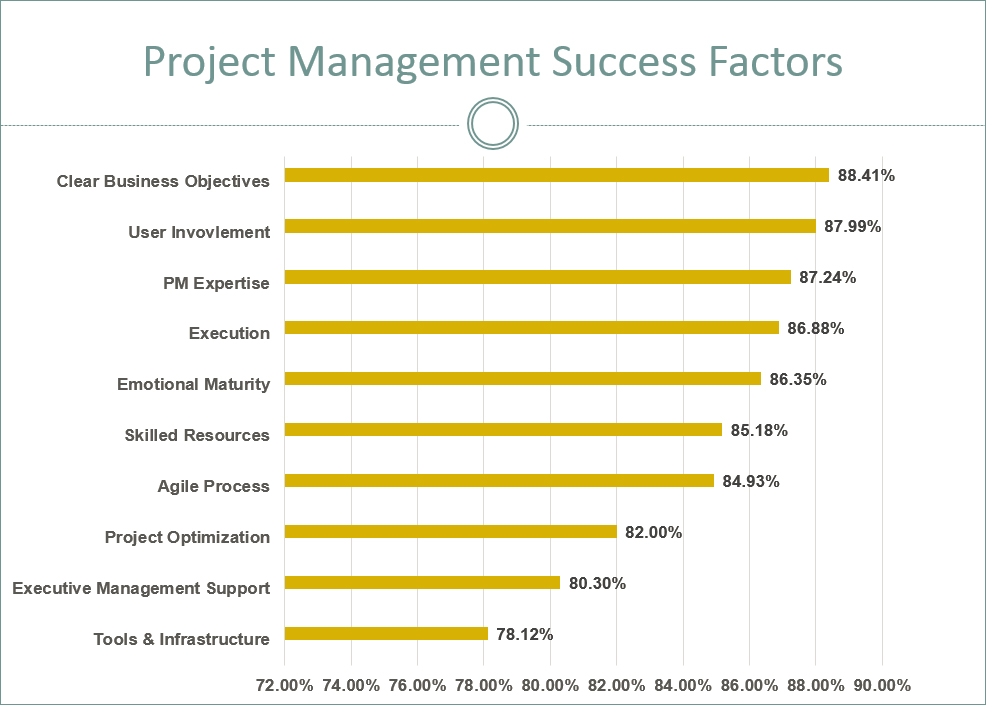
From 2014 NUS-ISS survey results on project management success factors
What makes for the higher percentage of successes in projects in Singapore? Quoting one CEO of a large government agency #2, “the “can do” attitude of Singapore project managers and the "willingness of management to stick with challenging projects to try to make something good out of them” is the key reasons.
Sharing some of the insights from the survey, out of ten factors, the top three which had the greatest influence on the outcome of the projects were Clear Business Objectives #3, User Involvement #4, and Project Management Expertise#5. What is surprising is that Executive Management Support, which consistently ranks amongst the top three factors in international studies, was ranked in the bottom two in the NUS-ISS survey. We look further into these four factors.
1. Clear Business Objectives
Starting the project right means starting with clearly articulated and documented business goals and objectives. Projects do not exist in a vacuum but in an ecosystem within programmes and the IT Portfolio. Understanding what this means gives context to the project and clarity to the expected project deliverables. On a day-to-day basis, it is the business imperative that guides decisions on scope changes, prioritisation and scheduling.
2. User Involvement
User involvement is a substantively important factor for project success. Right user selection is the main contributor for its high importance. Whilst selection is typically based on domain expertise, other criteria in terms of logical thinking abilities, decision making authority and desire to participate contribute to selecting the right user. When identified, management needs to support by availing this person for the project.
3. Project Management Expertise
In project management expertise, skills of planning, executing, leadership and decision making were the main contributors to this factor. Relevant business domain knowledge, which is highly valued by the senior management did not surface as a strong contributor. However, Project Managers need to learn to “speak” in the language of business, to bridge the gap between business and technical domains. This is a good stakeholder management practice.
4. Executive Management Support
The lower ranking of Executive Management Support indicates that this is not a critical pain point. Supporting this are observations that senior management representatives in IT projects tend to see projects to completion, providing stability and continuity of the vision and in decision making. While seemingly prevalent in Singapore’s context, it cannot be taken for granted. Continued education and engagement of management representatives is advised.
|
Agile Adoption in Projects
Another key findingindicated that 67% of respondents were either not aware ofor had never used agile methods in projects. Of those who had used agile methods, their key challengeswere managing frequent change of requirements and the stakeholders’ involvement and expectations. Awareness and in-depth understanding of the agile methods enables mind-set change and equips project teams to adopt relevant agile practices for improving success of their projects.
|
If you are interested in improving your project management skills, visit here to see our full suite of project management courses.
References (#)
#1 CHAOS report 2013
#2 Dr. Chong Yoke Sin (CEO of IHIS) in her talk at the SCS AGM in 2014
#3 Clear Business Objectives is defined as having clarity of project goal, business value, stakeholder consensus on project success definitions and measures of success.
#4 User Involvement is defined as including the users in various project management and development activities to establish a common understanding between users and the project team
#5 Project Management Expertise includes basic project managements skills and ability to manage up, down and across the organization